|

|

|
Return to Vintage Corvettes Home Page
Return to Vintage Corvettes Features Page
Publisher, The Corvette Story
Eight Seminal Moments in Corvette History
Definition of Seminal: Highly original and influencing the development of future events.
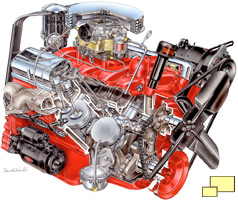
1) Small Block Chevy - Engine
Left: Cutaway drawings by David Kimble of the new small block engine.
It was a partnership made in high performance heaven - the Chevrolet Small Block engine made the Corvette famous and the Corvette made the Chevrolet Small Block engine famous.
It was introduced in 1955 and was also a major milestone in automotive engines. The engineering was advanced and featured a compact design, overhead valves and low production costs. Whenever a list of the world's most significant automobile engines is compiled, the Chevrolet small block is always included.
Although it has undergone many changes and updates, the engine we get with the 2024 C8 Stingray is a direct descendant to the V8 first available in 1955. Both feature in the block camshafts in an OHV design with the cylinders placed at 4.40 inch bore centers.
56 years after the debut of the first production small-block, on Tuesday, November 29, 2011 at the GM Performance Build Center in Wixom, Michigan, GM held a party to celebrate. Participants got to build the milestone 100,000,000th engine which is a 638-horsepower supercharged LS9 small block. It represents the fourth generation of the small block and as of 2011 it was the most powerful engine ever built by GM for a regular-production car. GM will preserve the engine as part of its historical collection.
2) 1957: Fuel Injection
Why fuel injection? The problem was that during long sustained high speed cornering, a situation often encountered in road racing, fuel in the carburetor bowls would slosh around and cause fuel starvation to the engine. Clearly a bad thing.
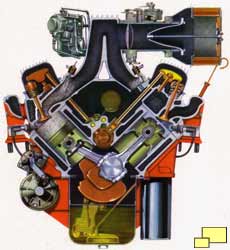 Chevrolet pulled something amazing out of the hat for 1957: Fuel Injection. First run in 1956 at the Sebring race, the Rochester Ramjet injection was an answer to Mercedes-Benz which featured fuel injection in the 1954 300SL. The innovation solved a fuel starvation problem caused by fuel sloshing while cornering with carbureted engines under race conditions. The fuel injection system is displayed in a cutaway drawing to the left.
Chevrolet pulled something amazing out of the hat for 1957: Fuel Injection. First run in 1956 at the Sebring race, the Rochester Ramjet injection was an answer to Mercedes-Benz which featured fuel injection in the 1954 300SL. The innovation solved a fuel starvation problem caused by fuel sloshing while cornering with carbureted engines under race conditions. The fuel injection system is displayed in a cutaway drawing to the left.
To keep this development in perspective, consider this: Almost all of the high priced supposedly advanced competition -- including Jaguar, Porsche, Ferrari and Lamborghini -- did not go with fuel injection until the 1970s or later. Mercedes-Benz, in 1955, did offer fuel injection in the 300SL - a more expensive car than the Corvette.
Left: Ad touting the advantages of fuel injection. Middle: GM Fuel Injection photo. Right: This one is a hoot. The marketing folks must have had a lot of fun poking fun at the Italians and the fact that they were not competitive regarding engine technology. Note the Ferrari like competition peering out jealously from under a car cover.
The fuel injection in 1957 was the start of Corvette's role as a halo car for GM; the Corvette would continue to serve as a showcase for the best of GM. With its introduction, the horsepower (283 hp) was equal to its cubic inch displacement of 283 cubic inches, the one horsepower per cubic inch milestone was achieved.
3) 1957: Four Speed Transmission
The Corvette started life with a significant disadvantage in the transmission department. For the first two years and well into the third year, the only choice was a two speed Powerglide transmission. At the time, four speed manuals were standard with even low cost sports cars such as MG, Triumph - even the lowly VW Beetle was so equipped.

The Corvette was available with a manual trans in 1955 but it was only a three speed. It was also a truck sourced part with not so great shifting characteristics and a non synchromesh first gear. So when a proper four speed became available in the Corvette in 1957, it was a big deal. The street cred for the Corvette amongst sports car enthusiasts had been established.
Left: GM was justifiably proud of the four speed transmission as seen in the 1967 ad.
4) 1963: Independent Rear Suspension
Since its inception, the Corvette has been GM's halo car - it usually featured new technology. The first clue was in the body material from the beginning: Fiberglass.
Another technological advance came in the form of an independent rear suspension (IRS) in 1963. This was a bold move on the part of GM. To put it into perspective, consider this. It wasn't until 1992 - 29 years - after the introduction of the 1963 'vette that a car with an IRS designed by Chrysler (the 1992 Viper) was available to the public.
The IRS was a radical move and positioned the Corvette as a serious road car. The improvement was dramatic and car enthusiasts from all backgrounds took notice. Overall, the handling was much better and so was the feel. The new Corvette was not only faster on the race track, it also felt better. By comparison, the earlier Corvettes felt more cumbersome. The steering feel, agility, responsiveness and "fun to drive" factor was such that even foreign car aficionados took notice.
5) 1965: Big Block Engine
We are all aware of the Corvette's bad boy reputation. Its source can be debated but one candidate is the Big Block motor that was featured in the late C2 and early C3 Corvettes. While not true, there were rumors that the big blocks would register on the Richter scale whenever driven nearby.
They started in late 1965 as a 396 cubic incher and then went to 427 cubic inches in 1966 via a bore and stroke increase. It stayed as a 427 mill and then went to 454 cubic inches in 1970; that would be the largest displacement engine that GM would offer in a Corvette. The last year for the big block, at least in its C2 / C3 format, was 1974. Horsepower rating was down to 270 hp.
6) 1968: Coke Bottle Shape
How the C3 Corvette got it's "Coke Bottle Shape" moniker. Notice the pinched in area just above the bottom of the coke bottle and a similar pinched in area on the doors of the Corvette.
The side view of the Corvette has a similar theme with the front and rear fenders. Notice also that both are a relatively narrow design.
The drawings are from actual patent filings; see https://patents.google.com/patent/USD212152S/en. The inventor is Henry G. Haga and it is assigned to General Motors. Henry is in the Corvette Hall of Fame.
It's important to note that much of the design philosophy of the 1968 C3 continued through the C7 generation which ended in 2019.
7) C5: Advanced Technology
If you were to look for when the most significant changes in Corvette technology took place, your search would end with the introduction of the C5 Corvette in 1997.
The automotive world changed significantly during the reign of the C4 Corvette. Computers had not only become part of the cars but perhaps more importantly were being used extensively in the design and engineering process.
Performance car standards, along with customer's expectations, had changed. Previously high performance meant comfort sacrifices. Bone rattling, noisy and uncomfortable rides was the price of speed and there was no getting around it. But technology had changed and when the latter part of the 1990s arrived, going fast did not require self imposed torture.
The C5 was introduced in 1997. It was an entirely new car; more so than any other Corvette generation in that all major elements - the drivetrain, the chassis and the body - had not appeared before.
Something else was new: When describing the C5, road testers used the word "refined", which was not how previous Corvettes were labeled. It's not that the Corvette was going soft in its later years; the difference was in the state of the automotive art.
The reason behind the significant improvements can be found in the utilization of CAD (Computer Aided Design) and CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) as part of the development process.
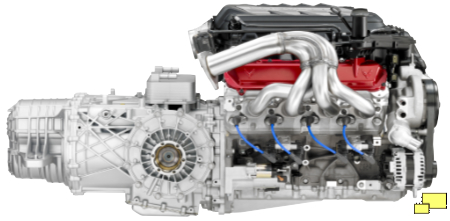
Of the many innovations of the C5, the rear transaxle was at the top of the list. With a transaxle design, the transmission and the differential are located in a combined case at the rear axle. This was the same layout used in the Porsche 944 and Ferrari Daytona. The goal was improved balance; with the weight shifted more to the rear a better front / rear weight distribution was possible. In the case of the C5, weight distribution was 51% front / 49% rear which is close to ideal and an excellent statistic for a front engine car. Another advantage of the rear transaxle was more space in the cockpit area, which resolved a complaint from C4 owners who felt that the footwell areas was too small. Note the torque tube in front of the transaxle and to the right in the above photo. It mechanically coupled the engine to the transaxle which improved handling response, delivering that wonderful and often elusive "sports car feel".
8) C8: Mid-Engine Layout
By the time the C7 generation was coming to an end, an obvious truth appeared. The Corvette, if it were to remain competitive as a performance car, needed to go mid engine.
And so Zora Arkov-Duntov's dream of a mid engine production Corvette became a reality.
The extraordinary change was the beginning of a new Corvette era. It immediately became recognized not only as one of the great sports cars, it also became one of the great performance cars.
GM did not stop there. Some truly significant performance improvements followed, including the 2023 Z06, the 2024 E-Ray and the (recently announced) 2025 ZR1.
Click on any image to view a larger image